evenlySpaceCurve
Below is a basic demonstration of the features of the evenlySpaceCurve function.
Contents
clear; close all; clc;
Syntax
[Vg] = evenlySpaceCurve(V,pointSpacing,interpPar,closeLoopOpt,indMust);
Description
The evenlySpaceCurve function samples a curve evenly using the point spacing pointSpacing. The curve is parameterized using curve distance and can be closed loop if closeLoopOpt==1 (default=0). The resampling is performed using interpolation based on the method specified by interpPar. Available methods are those associated with interp1 i.e.: 'linear', 'nearest', 'next', 'previous', 'spline', 'pchip' (default), 'cubic', and also the custom 'biharmonic' method. Alternatively interpPar my be set as a scalar in the range 0-1 to use the csaps method for cubic spline based smoothening. The 5th input is indMust which defines indices of "must points", i.e. points on the curve which the user can demand to be included in the output curve. The interpolation, if must points are used, splits the curve in segments using the must points and interpolates for each segment using the point spacing provided.
The default values for the optional parameters are: pointSpacing -> curve length divided by number of input points interpPar -> 'pchip' closeLoopOpt -> 0 indMust -> [ ], empty
See also: evenlySampleCurve, interp1, csaps, biharmonicSplineInterpolation
Examples
Plot settings
markerSize1=25; markerSize2=35; lineWidth=2;
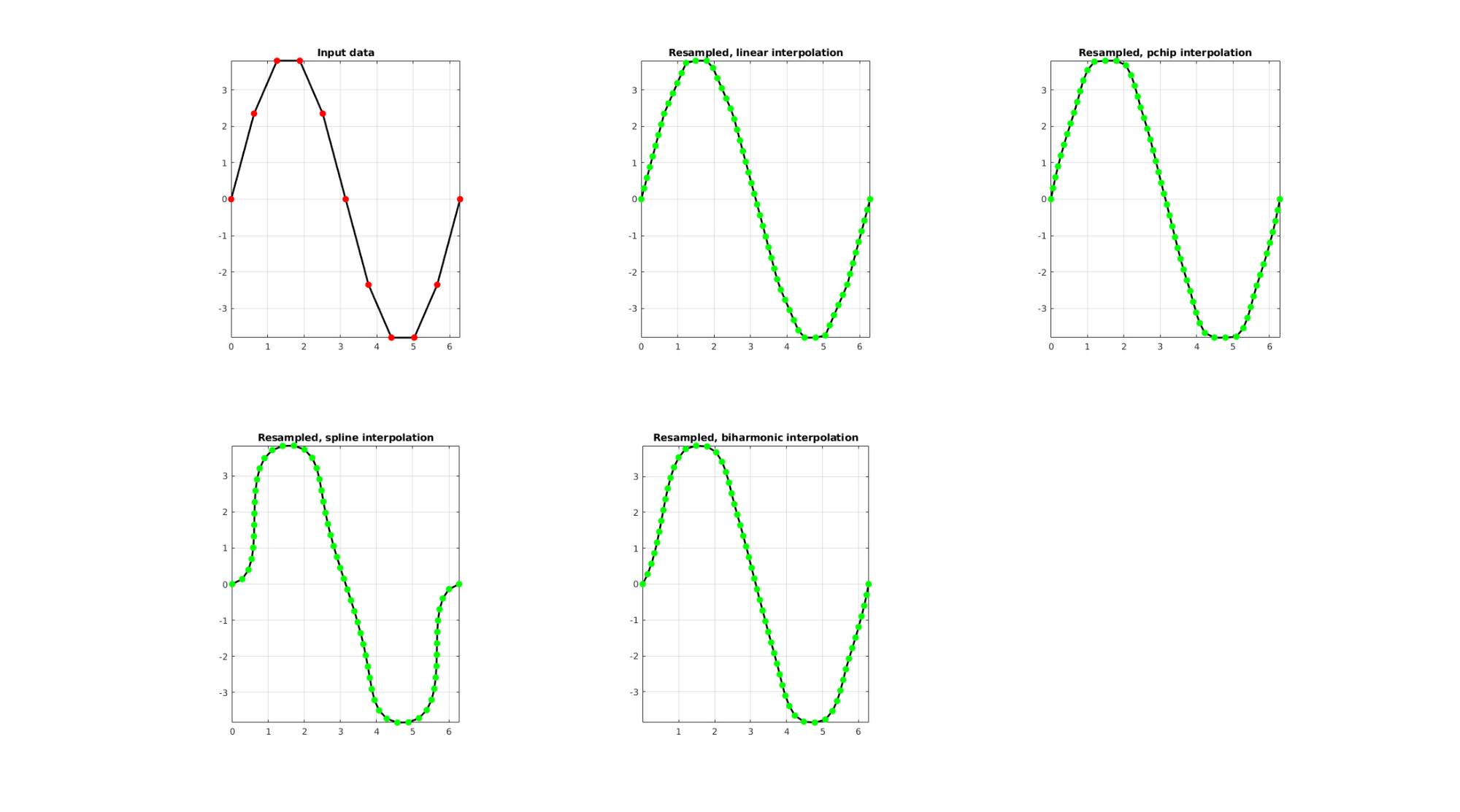
EXAMPLE 1: Evenly sampling a curve
%Simulating the case of an unevenly sampled curve
ns=11;
x=linspace(0,2*pi,ns);
y=4*sin(x);
V=[x(:) y(:)];
Below the original and resampled curves are shown. Note that the original curve is sampled evenly allong the x-axis but is not evenly sampled allong the curve (point spacing not even). For instance the spacing is smallest in flat regions and lowest in steep regions.Various interpolation methods are shown.
interpMethods={'linear','pchip','spline','biharmonic'};
closeLoopOpt=0; %Option for closed curve
pointSpacing=0.3; %New number of points
cFigure;
subplot(2,3,1); hold on;
title('Input data');
plotV(V,'k-','MarkerSize',markerSize1,'lineWidth',lineWidth);
plotV(V,'r.','MarkerSize',markerSize1,'lineWidth',lineWidth);
view(2); grid on; axis equal; axis tight; box on;
drawnow;
for q=1:1:numel(interpMethods)
[Vg]=evenlySpaceCurve(V,pointSpacing,interpMethods{q},closeLoopOpt);
subplot(2,3,q+1); hold on;
title(['Resampled, ',interpMethods{q},' interpolation']);
plotV(Vg,'k-','MarkerSize',markerSize1,'lineWidth',lineWidth);
plotV(Vg,'g.','MarkerSize',markerSize1,'lineWidth',lineWidth);
view(2); grid on; axis equal; axis tight; box on;
end
drawnow;
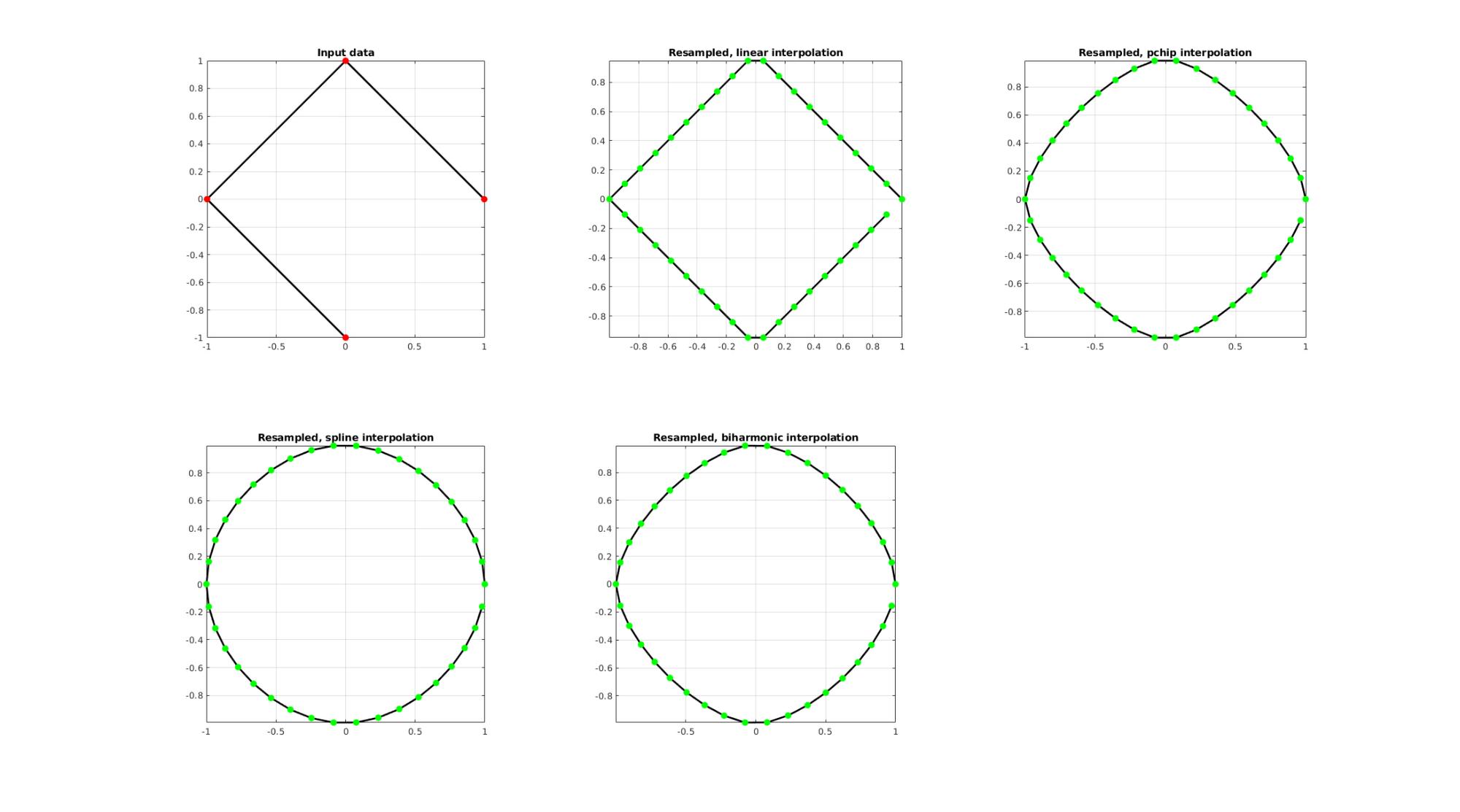
EXAMPLE 2: Upsample a closed polygon
%Simulating the case of an unevenly sampled curve ns=4; t=linspace(0,2*pi,ns+1)'; t=t(1:end-1);%+0.25*pi; V=[cos(t) sin(t)];
Below the original and resampled curves are shown. Note that the original curve is sampled evenly allong the x-axis but is not evenly sampled allong the curve (point spacing not even) For instance the spacing is smallest in flat regions and lowest in steep regions.Various interpolation methods are shown.
interpMethods={'linear','pchip','spline','biharmonic'};
closeLoopOpt=1; %Option for closed curve
pointSpacing=0.15; %New number of points
cFigure;
subplot(2,3,1); hold on;
title('Input data');
plotV(V,'k-','MarkerSize',markerSize1,'lineWidth',lineWidth);
plotV(V,'r.','MarkerSize',markerSize1,'lineWidth',lineWidth);
view(2); grid on; axis equal; axis tight; box on;
drawnow;
for q=1:1:numel(interpMethods)
[Vg]=evenlySpaceCurve(V,pointSpacing,interpMethods{q},closeLoopOpt);
subplot(2,3,q+1); hold on;
title(['Resampled, ',interpMethods{q},' interpolation']);
plotV(Vg,'k-','MarkerSize',markerSize1,'lineWidth',lineWidth);
plotV(Vg,'g.','MarkerSize',markerSize1,'lineWidth',lineWidth);
view(2); grid on; axis equal; axis tight; box on;
end
drawnow;
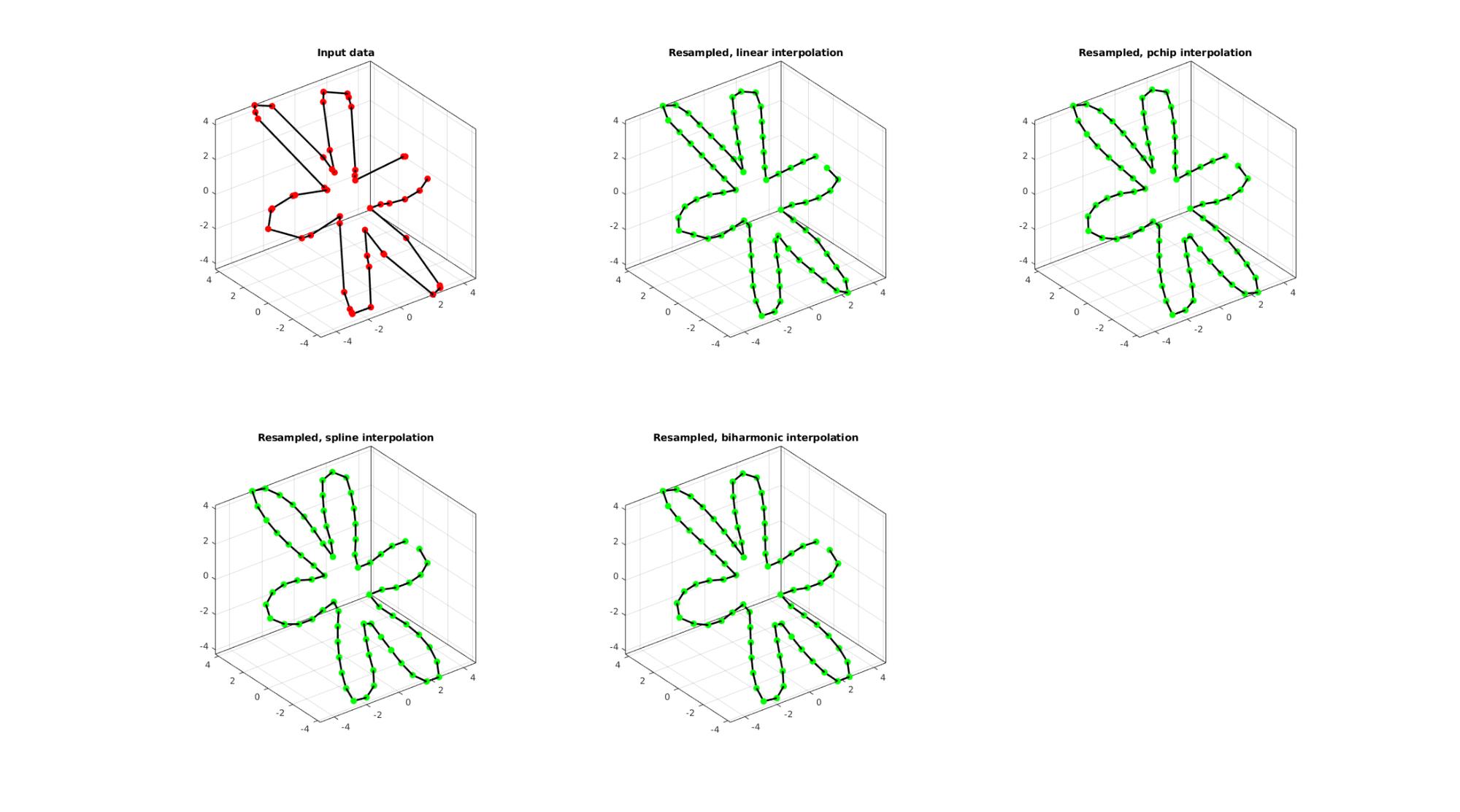
EXAMPLE 3: Evenly sampling a closed 3D curve
%Simulating the case of an unevenly sampled loop curve ns=50; t=sort(linspace(0,2*pi,ns)+pi/10*rand(1,ns)); t=unique(t); %removing double points t=t(t<2*pi);%Removing 2*pi points since they are the same as the 0 point r=3+2.*cos(6*t); [x,y] = pol2cart(t,r); z=y; V=[x(:) y(:) z(:)];
Below the original and resampled curves are shown. Note that the original curve is sampled evenly allong the x-axis but is not evenly sampled allong the curve (point spacing not even) For instance the spacing is smallest in flat regions and lowest in steep regions.Various interpolation methods are shown.
interpMethods={'linear','pchip','spline','biharmonic'};
closeLoopOpt=1; %Option for closed curve
pointSpacing=0.8; %New number of points
cFigure;
subplot(2,3,1); hold on;
title('Input data');
plotV(V,'k-','MarkerSize',markerSize1,'lineWidth',lineWidth);
plotV(V,'r.','MarkerSize',markerSize1,'lineWidth',lineWidth);
view(3); grid on; axis equal; axis tight; box on;
drawnow;
for q=1:1:numel(interpMethods)
[Vg]=evenlySpaceCurve(V,pointSpacing,interpMethods{q},closeLoopOpt);
subplot(2,3,q+1); hold on;
title(['Resampled, ',interpMethods{q},' interpolation']);
plotV(Vg,'k-','MarkerSize',markerSize1,'lineWidth',lineWidth);
plotV(Vg,'g.','MarkerSize',markerSize1,'lineWidth',lineWidth);
view(3); grid on; axis equal; axis tight; box on;
end
drawnow;
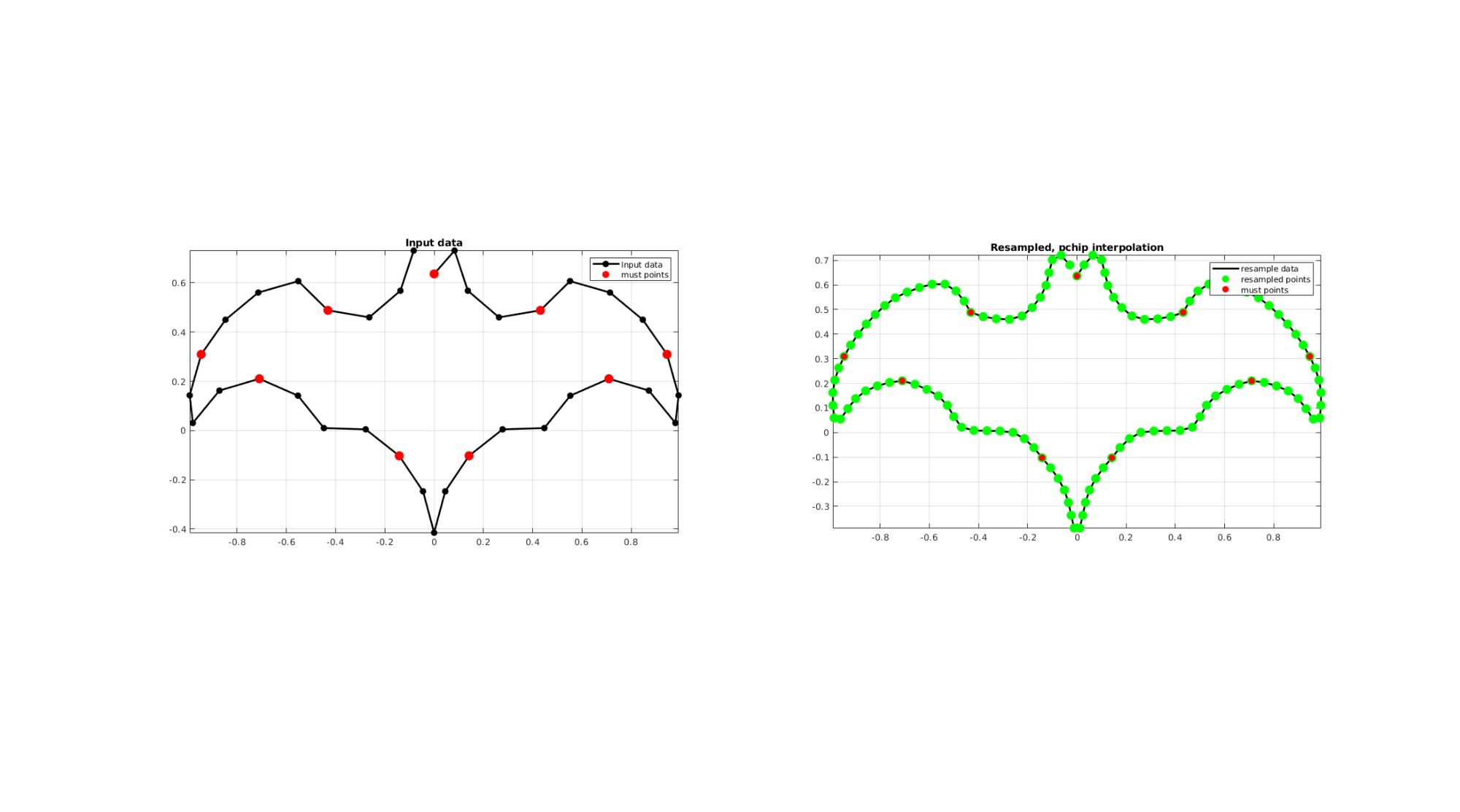
EXAMPLE 4: Using must points
% Creating curve V=batman(36); interpMethod='pchip'; closeLoopOpt=1; %Option for closed curve pointSpacing=0.05; %New number of points indMust=[1:4:size(V,1)]; [Vg]=evenlySpaceCurve(V,pointSpacing,interpMethod,closeLoopOpt,indMust); cFigure; subplot(1,2,1); hold on; title('Input data'); hp(1)=plotV(V,'k.-','MarkerSize',markerSize1,'lineWidth',lineWidth); hp(2)=plotV(V(indMust,:),'r.','MarkerSize',markerSize2); legend(hp,{'Input data','must points'}); grid on; axis equal; axis tight; box on; subplot(1,2,2); hold on; title(['Resampled, ',interpMethod,' interpolation']); hp(1)=plotV(Vg,'k-','MarkerSize',markerSize1,'lineWidth',lineWidth); hp(2)=plotV(Vg,'g.','MarkerSize',markerSize2); hp(3)=plotV(V(indMust,:),'r.','MarkerSize',markerSize1); grid on; axis equal; axis tight; box on; legend(hp,{'resample data','resampled points','must points'}); drawnow;

GIBBON www.gibboncode.org
Kevin Mattheus Moerman, [email protected]
GIBBON footer text
License: https://github.com/gibbonCode/GIBBON/blob/master/LICENSE
GIBBON: The Geometry and Image-based Bioengineering add-On. A toolbox for image segmentation, image-based modeling, meshing, and finite element analysis.
Copyright (C) 2019 Kevin Mattheus Moerman
This program is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU General Public License for more details.
You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License along with this program. If not, see http://www.gnu.org/licenses/.