polyExtrude
Below is a demonstration of the features of the polyExtrude function
Contents
Syntax
[F_tri,V_tri]=polyExtrude(Vc,cPar);
Description
The polyExtrude function can be used to extrude polygons to obtain surface patch data and generate CAD like model geometry. See also: polyLoftLinear
Examples
clear; close all; clc;
Plot settings
fontSize=15; lineWidth=4;
Example: EXTRUDING A PLANAR POLYGON
Creating an example polygon (or sketch)
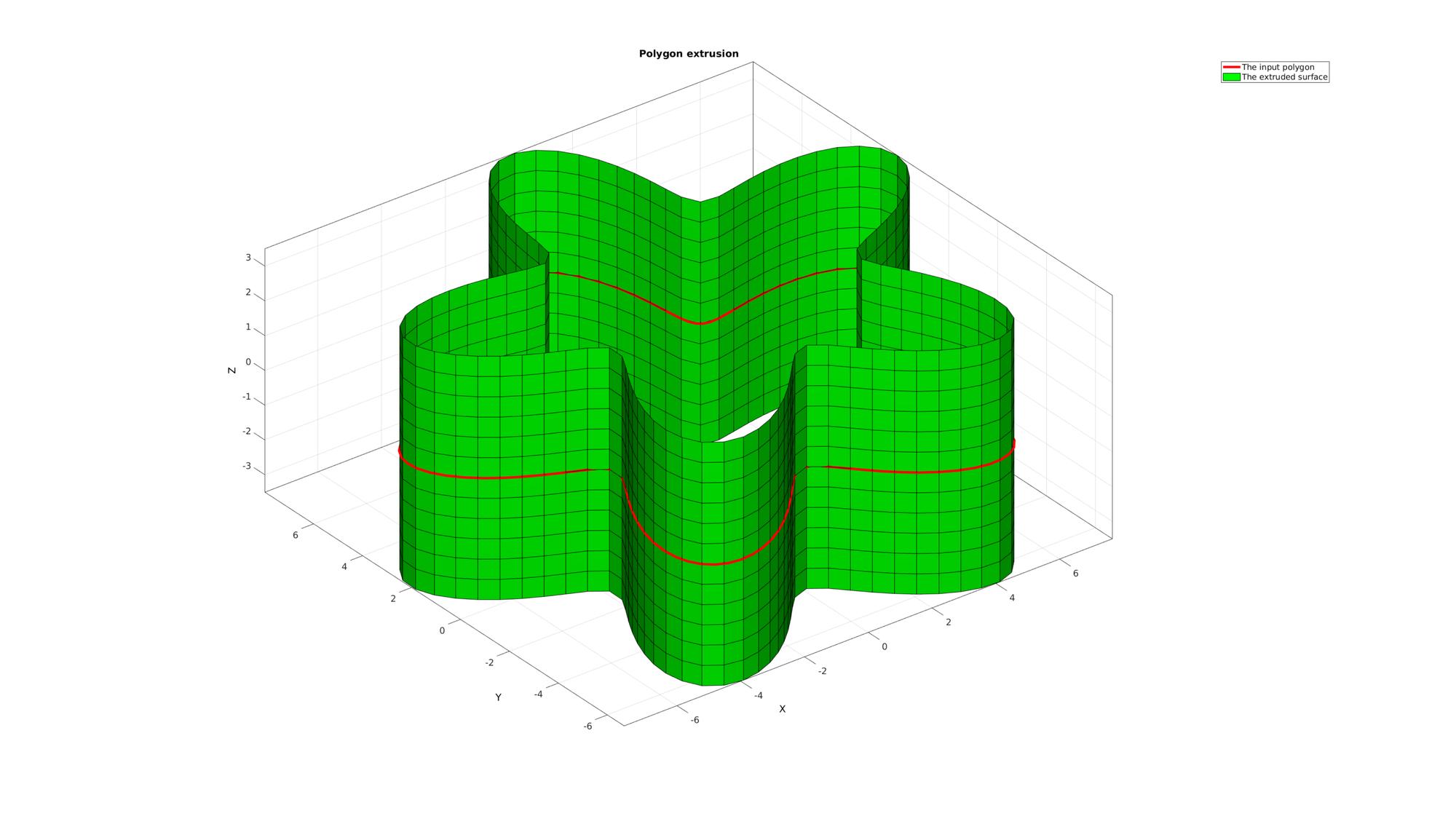
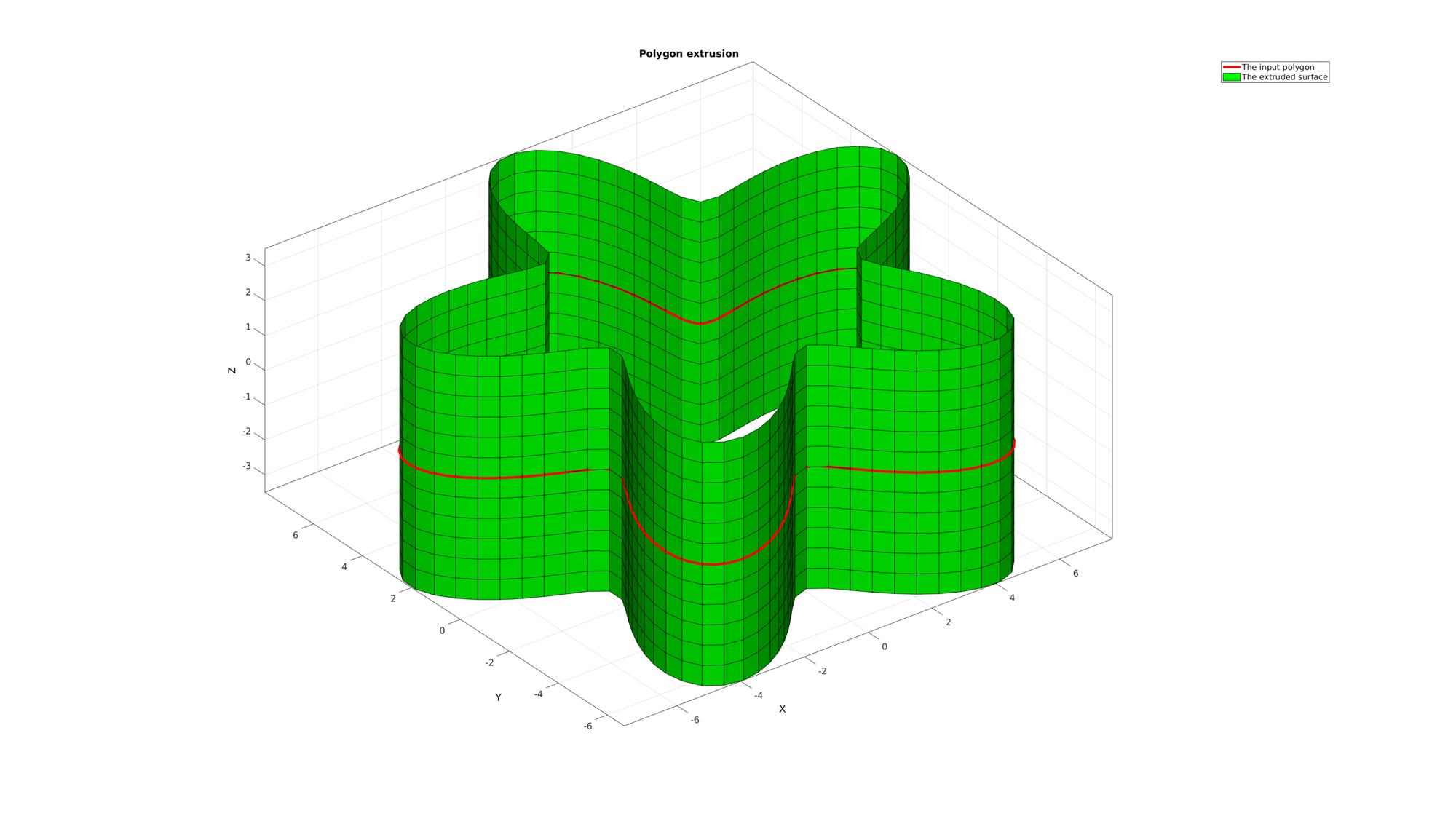
ns=150; t=linspace(0,2*pi,ns); t=t(1:end-1); r=6+2.*sin(5*t); [x,y] = pol2cart(t,r); z=zeros(size(x)); Vc=[x(:) y(:) z(:)];
Extruding polygon to obtain the surface model
cPar.pointSpacing=0.55;
cPar.depth=7;
cPar.patchType='quad';
cPar.dir=0;
cPar.closeLoopOpt=1;
[F,V]=polyExtrude(Vc,cPar);
Plotting results
cFigure; title('Polygon extrusion','FontSize',fontSize); hold on; hp1=plotV(Vc,'r-','lineWidth',lineWidth); hp2=gpatch(F,V,'g'); axisGeom(gca,fontSize); camlight headlight; legend([hp1 hp2],'The input polygon','The extruded surface'); drawnow;
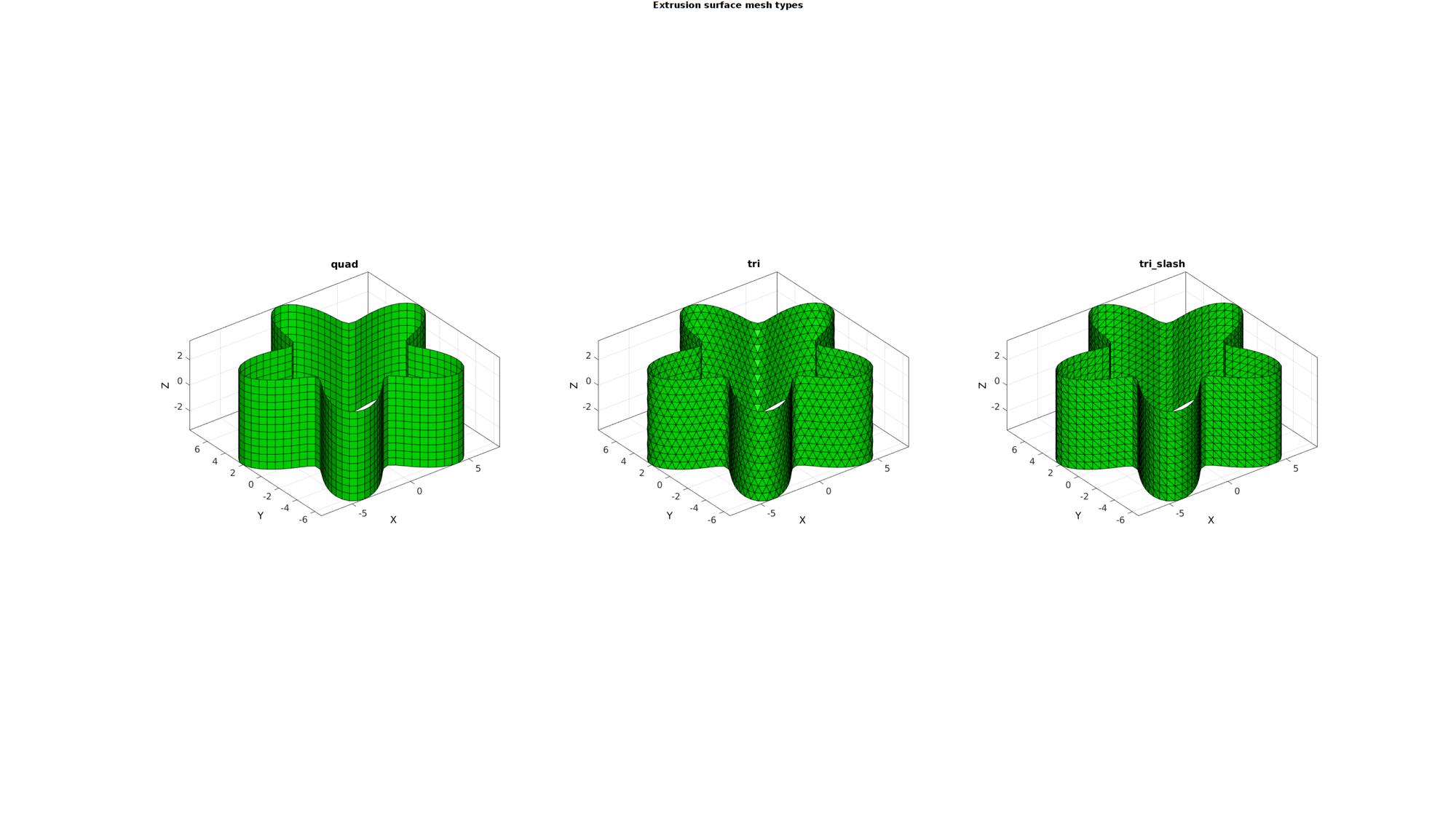
Exmaple: Mesh type control
Visualizing extrusion with all possible mesh types
patchTypes={'quad','tri','tri_slash'};
cFigure;
gtitle('Extrusion surface mesh types',fontSize);
for q=1:1:numel(patchTypes)
cPar.patchType=patchTypes{q};
[F,V]=polyExtrude(Vc,cPar);
%Visualizing mesh
subplot(1,numel(patchTypes),q);
title(patchTypes{q},'FontSize',fontSize,'Interpreter','none');
hold on;
gpatch(F,V,'g');
axisGeom(gca,fontSize);
camlight headlight;
end
drawnow;
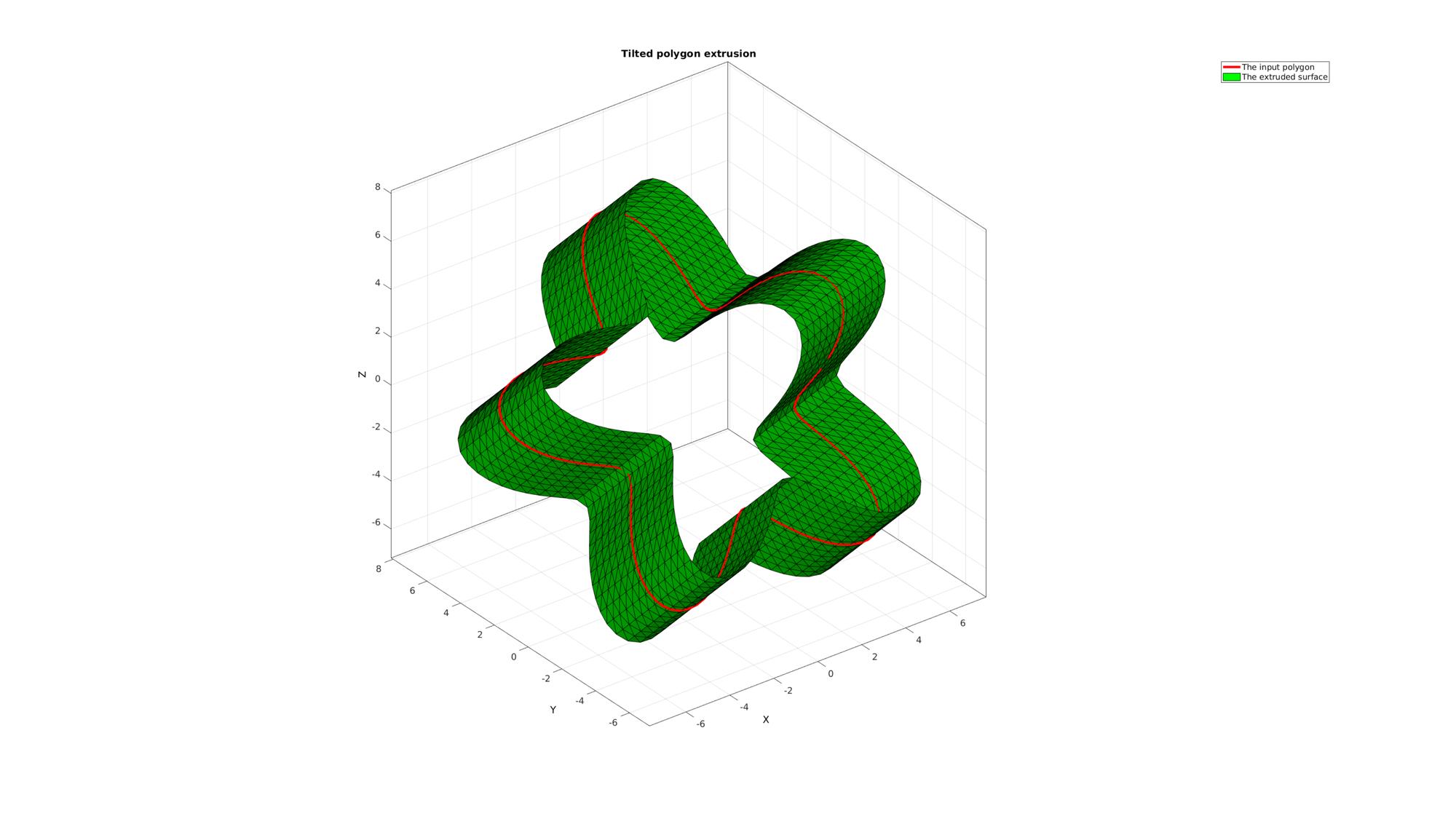
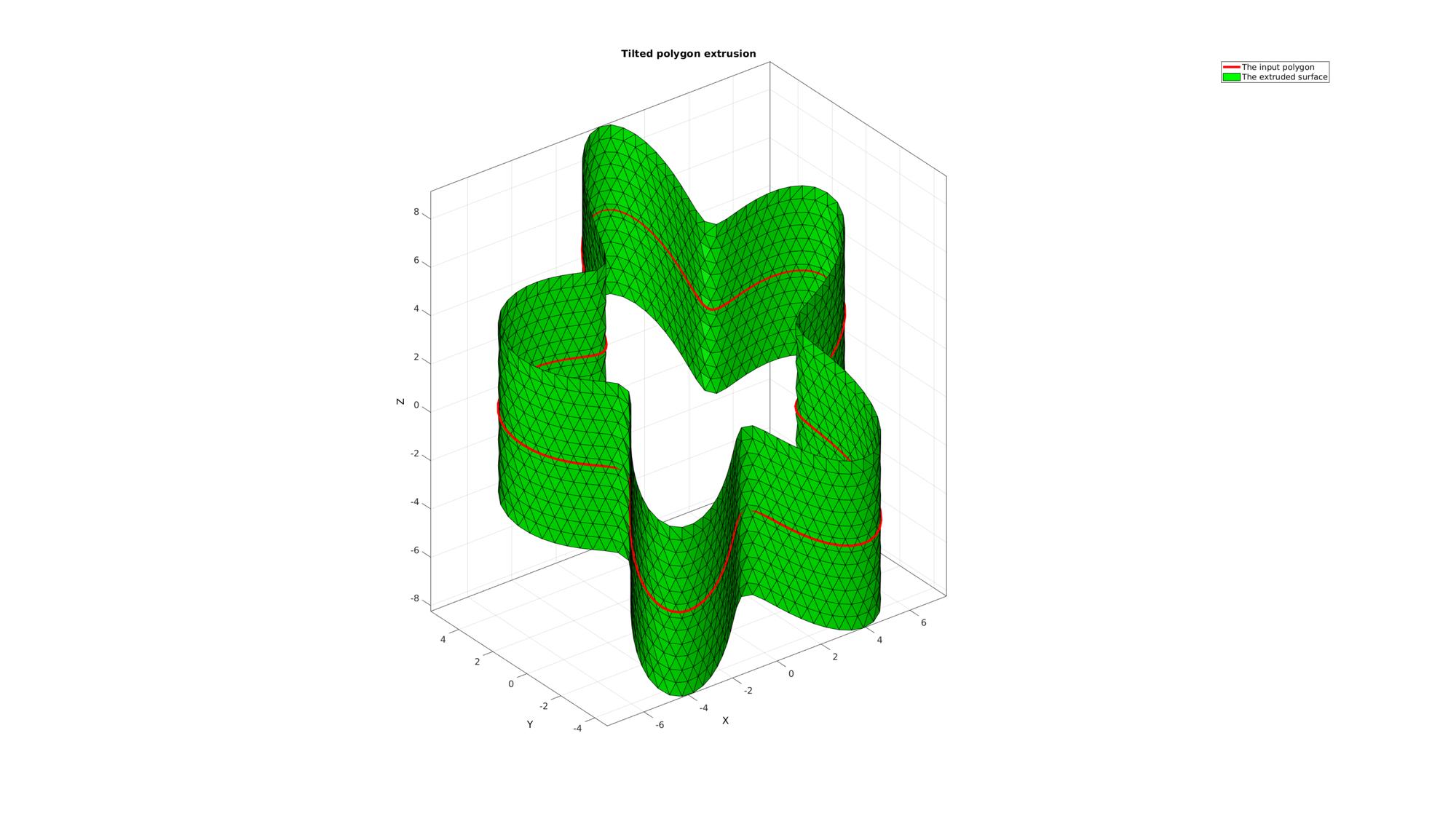
Example: EXTRUDING A TILTED PLANAR POLYGON
Creating an example of a rotated polygon
% Create rotation matrix E=[0.25*pi 0 0]; %Euler angles [R,~]=euler2DCM(E); %The rotation matrix % Rotate the polygon Vc=(R*Vc')';
Extruding model
clear cPar; cPar.pointSpacing=0.5; cPar.depth=7; cPar.patchType='tri_slash'; cPar.dir=0; cPar.closeLoopOpt=1; [F,V]=polyExtrude(Vc,cPar);
Plotting results
cFigure; title('Tilted polygon extrusion','FontSize',fontSize); hold on; hp1=plotV(Vc,'r-','lineWidth',lineWidth); hp2=gpatch(F,V,'g'); axisGeom(gca,fontSize); camlight headlight; legend([hp1 hp2],'The input polygon','The extruded surface'); drawnow;
Alternative extrusion direction direction
% Extruding model clear cPar; cPar.pointSpacing=0.5; cPar.depth=7; cPar.patchType='tri'; cPar.dir=0; cPar.n=[0 0 1]; cPar.closeLoopOpt=1; [F,V]=polyExtrude(Vc,cPar);
Plotting results
cFigure; title('Tilted polygon extrusion','FontSize',fontSize); hold on; hp1=plotV(Vc,'r-','lineWidth',lineWidth); hp2=gpatch(F,V,'g'); axisGeom(gca,fontSize); camlight headlight; legend([hp1 hp2],'The input polygon','The extruded surface'); drawnow;
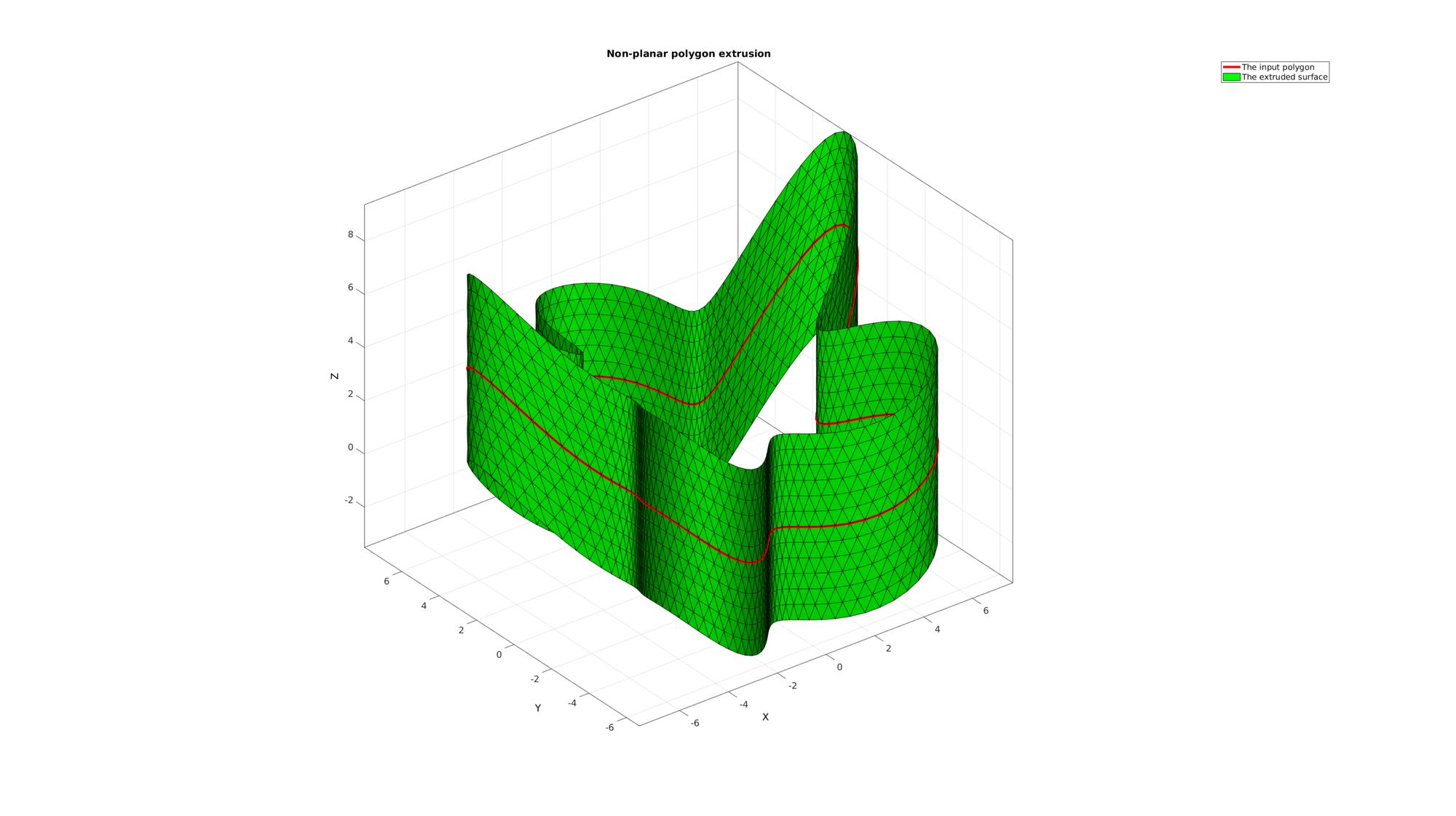
Example: EXTRUDING A NON-PLANAR POLYGON
Creating a non-planar polygon for extrusion
ns=150; t=linspace(0,2*pi,ns); t=t(1:end-1); r=6+2.*sin(5*t); [x,y] = pol2cart(t,r); z=1/10*x.^2; Vc=[x(:) y(:) z(:)];
% Extruding model clear cPar; cPar.numSteps=13; cPar.depth=7; cPar.patchType='tri'; cPar.dir=0; cPar.closeLoopOpt=1; [F,V]=polyExtrude(Vc,cPar);
Plotting results
cFigure; title('Non-planar polygon extrusion','FontSize',fontSize); hold on; hp1=plotV(Vc,'r-','lineWidth',lineWidth); hp2=gpatch(F,V,'g'); axisGeom(gca,fontSize); camlight headlight; legend([hp1 hp2],'The input polygon','The extruded surface'); drawnow;

GIBBON www.gibboncode.org
Kevin Mattheus Moerman, [email protected]
GIBBON footer text
License: https://github.com/gibbonCode/GIBBON/blob/master/LICENSE
GIBBON: The Geometry and Image-based Bioengineering add-On. A toolbox for image segmentation, image-based modeling, meshing, and finite element analysis.
Copyright (C) 2019 Kevin Mattheus Moerman
This program is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU General Public License for more details.
You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License along with this program. If not, see http://www.gnu.org/licenses/.