subTriDual
Below is a demonstration of the features of the subTriDual function
Contents
- Syntax
- Description
- Examples
- Example: Illustrating the refinement process
- Example: Refining a closed surface
- Showing downside of subTriDual for coarse meshes with sharp angles
- Example: Refining a local region of a mesh
- Example: Refining a local region of a sphere mesh
- Example Smoothing the mesh
- Example: Keeping track of surface data e.g. color
- Example: use for non-closed 3D surfaces with voids
- Example: Iterative refinement
clear; close all; clc;
Syntax
[Ft,Vt,C_type,indIni,Ct]=subTriDual(F,V,logicFaces,C);
Description
This function refines the surface region defined by the logic logicFaces, belonging to the surface given by the faces F and vertices V. The region is refined by: 1) taking the dual tesselation, 2) retriangulating the dual mesh to include the original points.
The input consists of: F: the faces V: the vertices logicFaces: A logic for the faces requiring refinement C: color data on either the faces or the vertices
The ouput can consist of: FT: Faces VT: Vertices C_type: Color/label for triangle type, i.e. original (1), refined (2), or boundary (3) indIni: Indices for original points C_new: New color data for faces or vertices
Examples
Plot settings
fontSize=15; cMap=gjet(4); faceAlpha=0.5; plotColor1=cMap(1,:); plotColor2=cMap(2,:); plotColor3=cMap(4,:); faceColor1=0.5*ones(1,3); edgeWidth=2; markerSize=25;
Example: Illustrating the refinement process
Building example geometry
%Defining geodesic dome r=1; %sphere radius n=1; %Refinements [F,V,~]=geoSphere(n,r);
Refine surface region using subTriDual
[Ft,Vt,C_type,indIni,C_new]=subTriDual(F,V); E=patchEdges(Ft,Vt); Ed=E(~any(ismember(E,indIni),2),:);
%Plotting results cFigure; subplot(1,3,1); hold on; title('Original','FontSize',fontSize); gpatch(F,V,'bw','k',1,edgeWidth); plotV(V,'b.','MarkerSize',markerSize); axisGeom(gca,fontSize); camlight headlight; ha=axis; axis off; subplot(1,3,2); hold on; title('Triangulated dual','FontSize',fontSize); gpatch(Ft,Vt,'w','k',1,0.5); gpatch(Ed,Vt,'none','r',1,edgeWidth); plotV(Vt(unique(Ed(:)),:),'r.','MarkerSize',markerSize); plotV(Vt(indIni,:),'b.','MarkerSize',markerSize); axisGeom(gca,fontSize); camlight headlight; axis off; axis(ha); subplot(1,3,3); hold on; title('Dual refined','FontSize',fontSize); gpatch(Ft,Vt,'gw','k',1,edgeWidth); plotV(Vt,'g.','MarkerSize',markerSize); axisGeom(gca,fontSize); camlight headlight; axis off; axis(ha); drawnow;
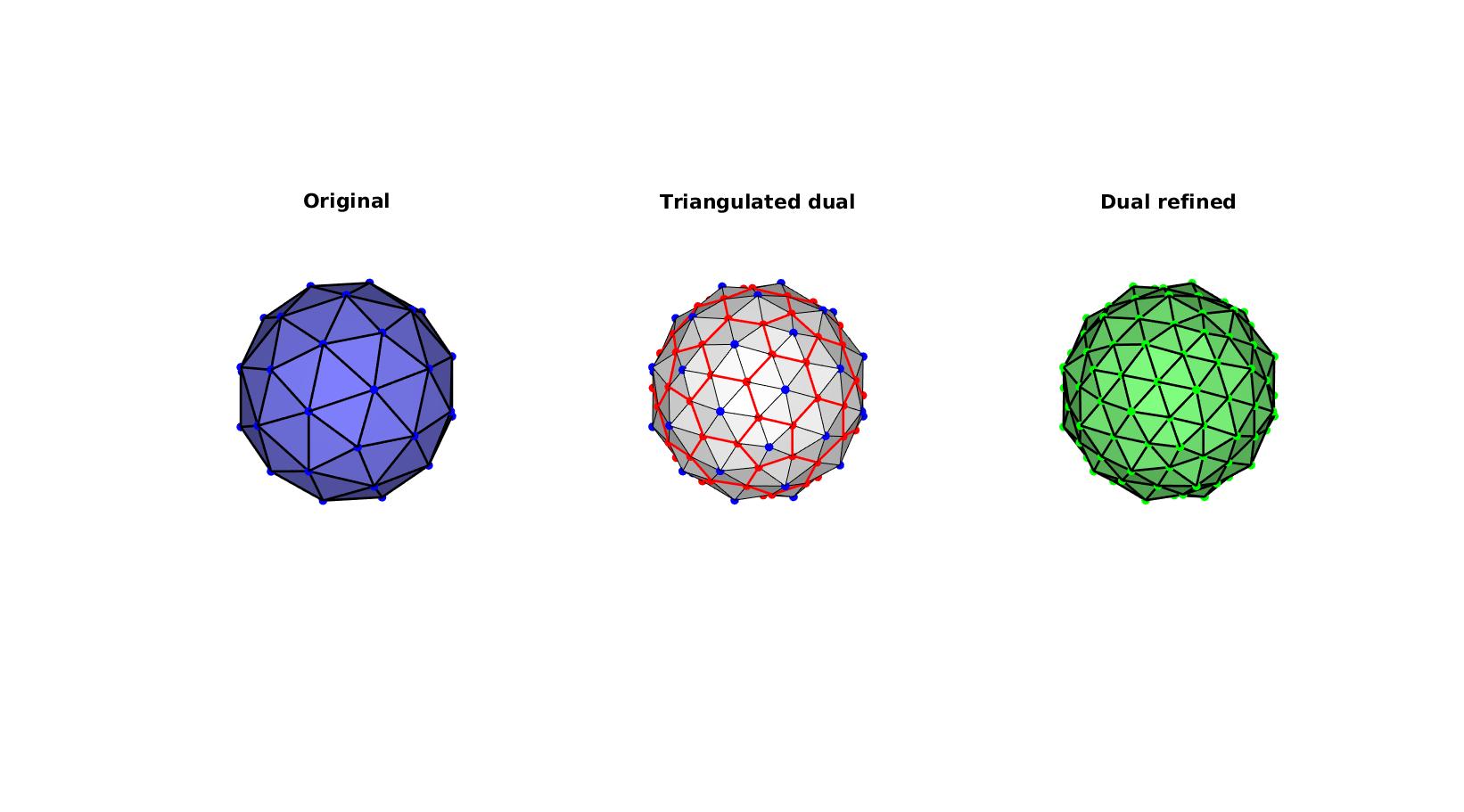
Example: Refining a closed surface
Building example geometry
r=1; %Radius rc=2.5; %Central radius nr=16; nc=25; [F,V]=patchTorus(r,nr,rc,nc,'tri');
Refine surface using subTriDual
[Ft,Vt,~,indIni]=subTriDual(F,V);
Plotting input surface model
cFigure; subplot(1,2,1); title('Input surface','FontSize',fontSize); hold on; gpatch(F,V,'g'); axisGeom(gca,fontSize); camlight headlight; subplot(1,2,2); title('Output surface','FontSize',fontSize); hold on; gpatch(Ft,Vt,'y'); plotV(Vt(indIni,:),'k.','MarkerSize',25); axisGeom(gca,fontSize); camlight headlight; colormap gjet; drawnow;
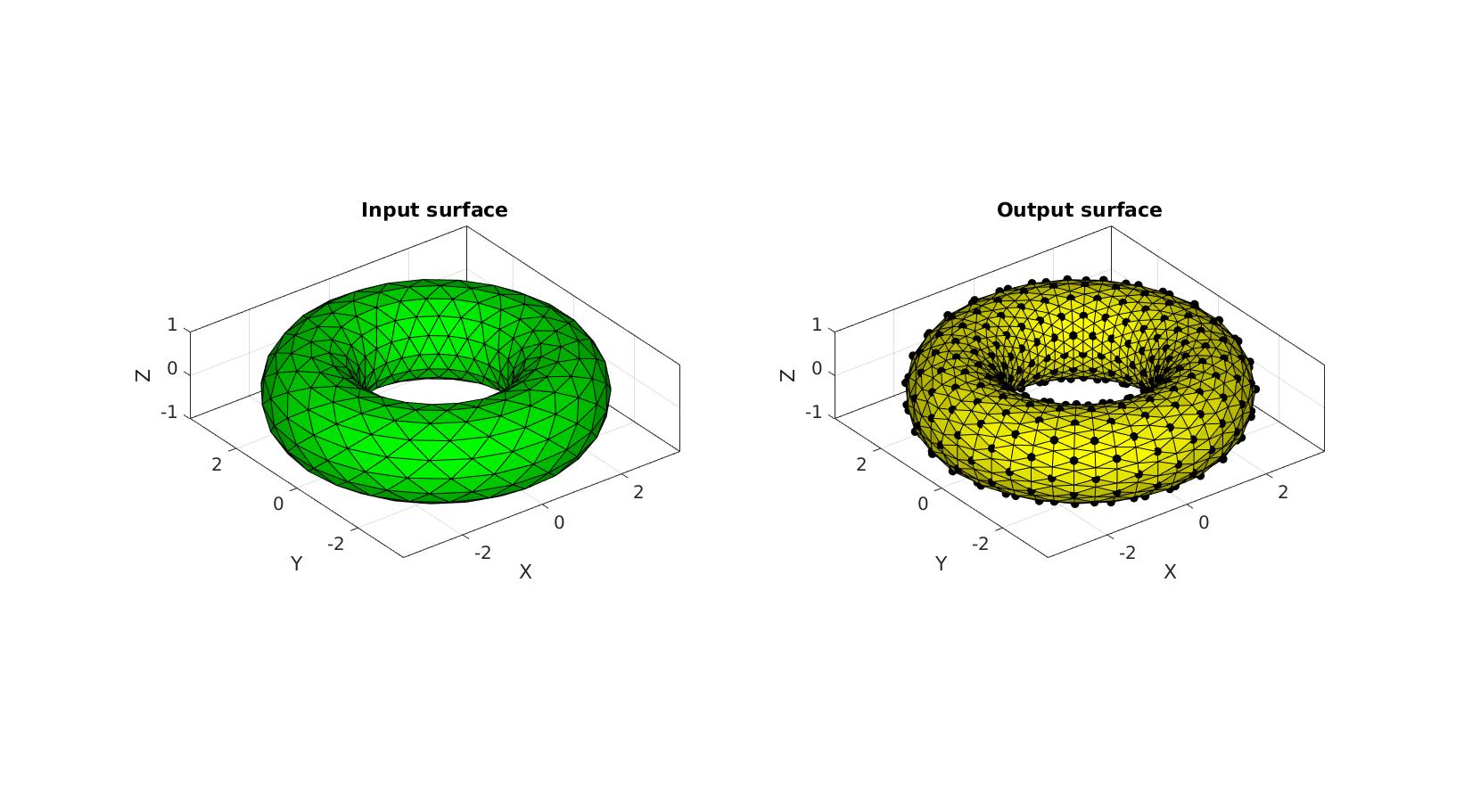
Showing downside of subTriDual for coarse meshes with sharp angles
m=sphereIm(1); [F,V]=im2patch(m,m>0,'vb'); [F,V]=quad2tri(F,V,'a'); [Ft,Vt,~,indIni]=subTriDual(F,V); E=patchEdges(Ft,Vt); Ed=E(~any(ismember(E,indIni),2),:);
%Plotting results cFigure; subplot(1,3,1); hold on; title('Original','FontSize',fontSize); gpatch(F,V,'bw','k',1,edgeWidth); plotV(V,'b.','MarkerSize',markerSize); axisGeom(gca,fontSize); camlight headlight; ha=axis; axis off; subplot(1,3,2); hold on; title('Triangulated dual','FontSize',fontSize); gpatch(F,V,'none','b',1,edgeWidth); gpatch(Ft,Vt,'w','k',1,0.5); gpatch(Ed,Vt,'none','r',1,edgeWidth); plotV(Vt(unique(Ed(:)),:),'r.','MarkerSize',markerSize); plotV(Vt(indIni,:),'b.','MarkerSize',markerSize); axisGeom(gca,fontSize); camlight headlight; axis off; axis(ha); subplot(1,3,3); hold on; title('Dual refined','FontSize',fontSize); gpatch(Ft,Vt,'gw','k',1,edgeWidth); plotV(Vt,'g.','MarkerSize',markerSize); axisGeom(gca,fontSize); camlight headlight; axis off; axis(ha); drawnow;
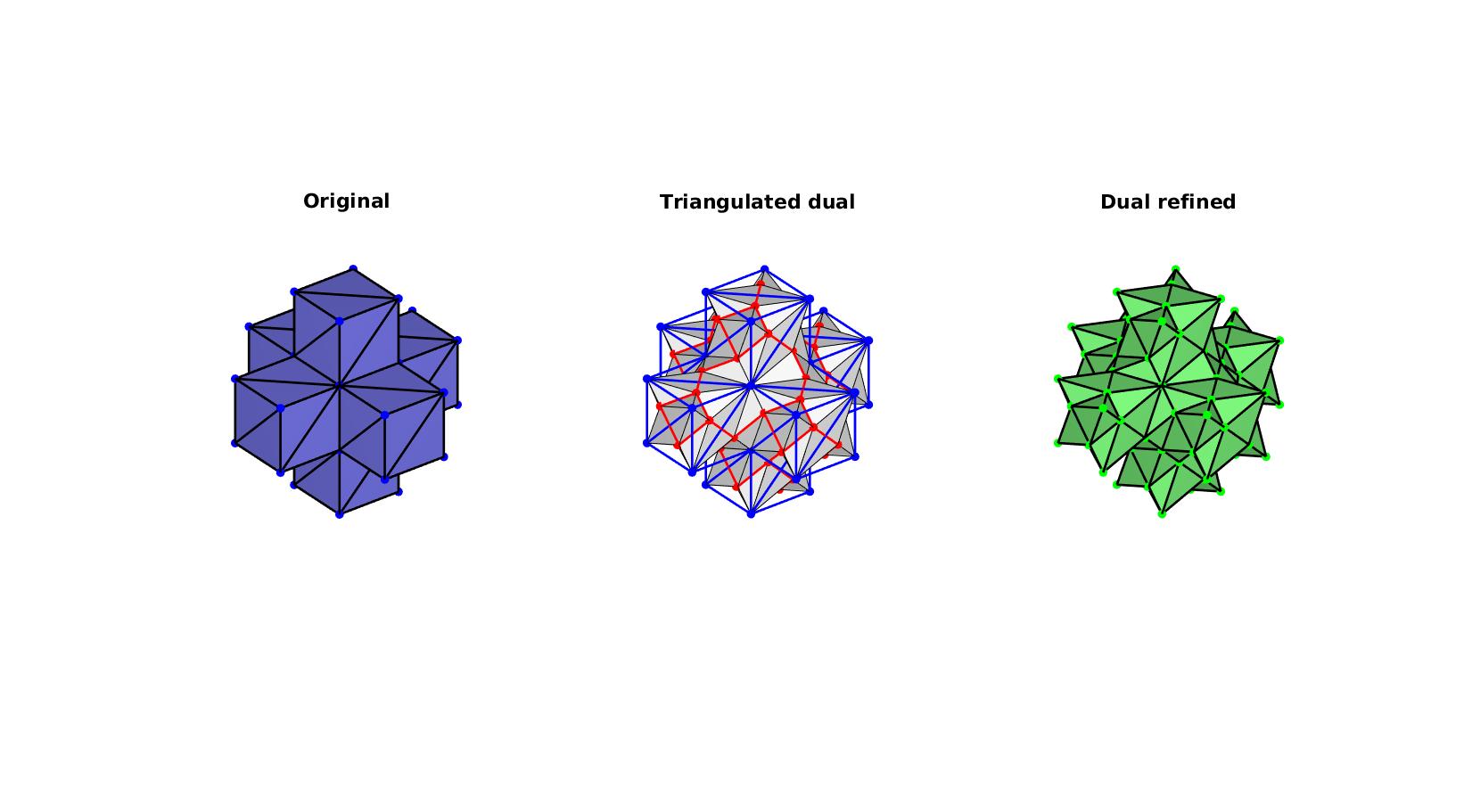
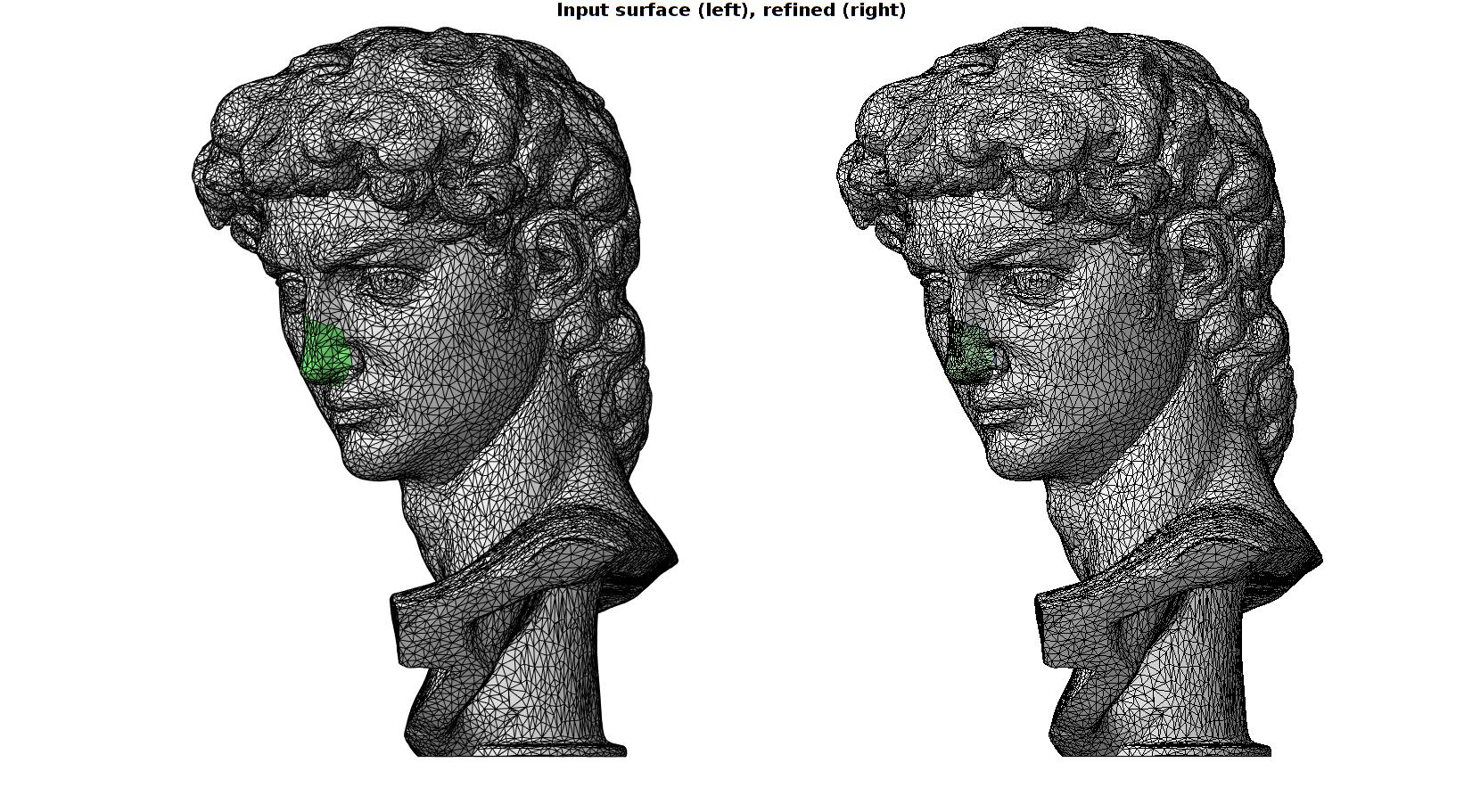
Example: Refining a local region of a mesh
Building example geometry
[F,V]=graphicsModels(9); % optionStruct2.pointSpacing=mean(patchEdgeLengths(F,V)); %Set desired point spacing % optionStruct2.disp_on=0; % Turn off command window text display % [F,V]=ggremesh(F,V,optionStruct2);
Refine surface using subTriDual
D=sqrt(sum((V-[64.9604 49.9194 220.751]).^2,2)); logicVertices=D<25; %Vertex logic logicFaces=any(logicVertices(F),2); %Convert to face logic logicFaces=triSurfLogicSharpFix(F,logicFaces,3); [Ft,Vt,C_type,indIni]=subTriDual(F,V,logicFaces); % %Smoothen newly introduced nodes % cPar.Method='HC'; %Smoothing method % cPar.n=50; %Number of iterations % cPar.RigidConstraints=indIni; %Constrained points % [Vt]=tesSmooth(Ft,Vt,[],cPar);
Plotting input surface model
cFigure; gtitle('Input surface (left), refined (right)',fontSize); subplot(1,2,1); hold on; gpatch(F,V,'w','k'); gpatch(F(logicFaces,:),V,'gw','k'); axisGeom(gca,fontSize); camlight headlight; view(0,0);zoom(2); axis off; subplot(1,2,2); hold on; gpatch(Ft,Vt,'w','k'); gpatch(Ft(C_type==2,:),Vt,'gw','k',0.5); gpatch(Ft(C_type==3,:),Vt,'bw','k'); axisGeom(gca,fontSize); camlight headlight; colormap(gca,gjet); %icolorbar; view(0,0);zoom(2); axis off; gdrawnow;

Example: Refining a local region of a sphere mesh
Building example geometry
%Defining geodesic dome r=1; %sphere radius n=3; %Refinements [F,V,~]=geoSphere(n,r);
Define face list for refinement
logicNodes=V(:,3)>0.6 | V(:,2)<-0.5; logicFaces=all(logicNodes(F),2);
Refine surface region using subTriDual
[Ft,Vt,C_type,indIni]=subTriDual(F,V,logicFaces);
Example Smoothing the mesh
Since subTriDual outputs indIni which are the indices for the initial nodes in the unrefined mesh, smoothing can be performed while holding on to these nodes, i.e. only the newly introduces nodes will be adjusted during smoothing.
%Smoothen newly introduced nodes cPar.Method='HC'; %Smoothing method cPar.n=50; %Number of iterations cPar.RigidConstraints=indIni; %Constrained points [Vt]=tesSmooth(Ft,Vt,[],cPar); %Smoothen boundary nodes on original mesh nodes E=patchBoundary(Ft(C_type==1,:)); indEdge=unique(E(:)); logicEdge=false(size(Vt,1),1); logicEdge(indEdge)=1; indRigid=find(~logicEdge); cPar.Method='HC'; cPar.n=50; cPar.RigidConstraints=indRigid; [Vt]=tesSmooth(Ft,Vt,[],cPar);
Plotting input surface model
cFigure; subplot(1,2,1); title('Input surface','FontSize',fontSize); hold on; gpatch(F,V,logicFaces); axisGeom(gca,fontSize); camlight headlight; subplot(1,2,2); title('Output surface','FontSize',fontSize); hold on; gpatch(Ft,Vt,C_type); % [hp]=patchNormPlot(Ft,Vt,0.25); plotV(Vt(indIni,:),'k.','MarkerSize',25); plotV(Vt(logicEdge,:),'y.','MarkerSize',50); colormap gjet; axisGeom(gca,fontSize); camlight headlight; drawnow;
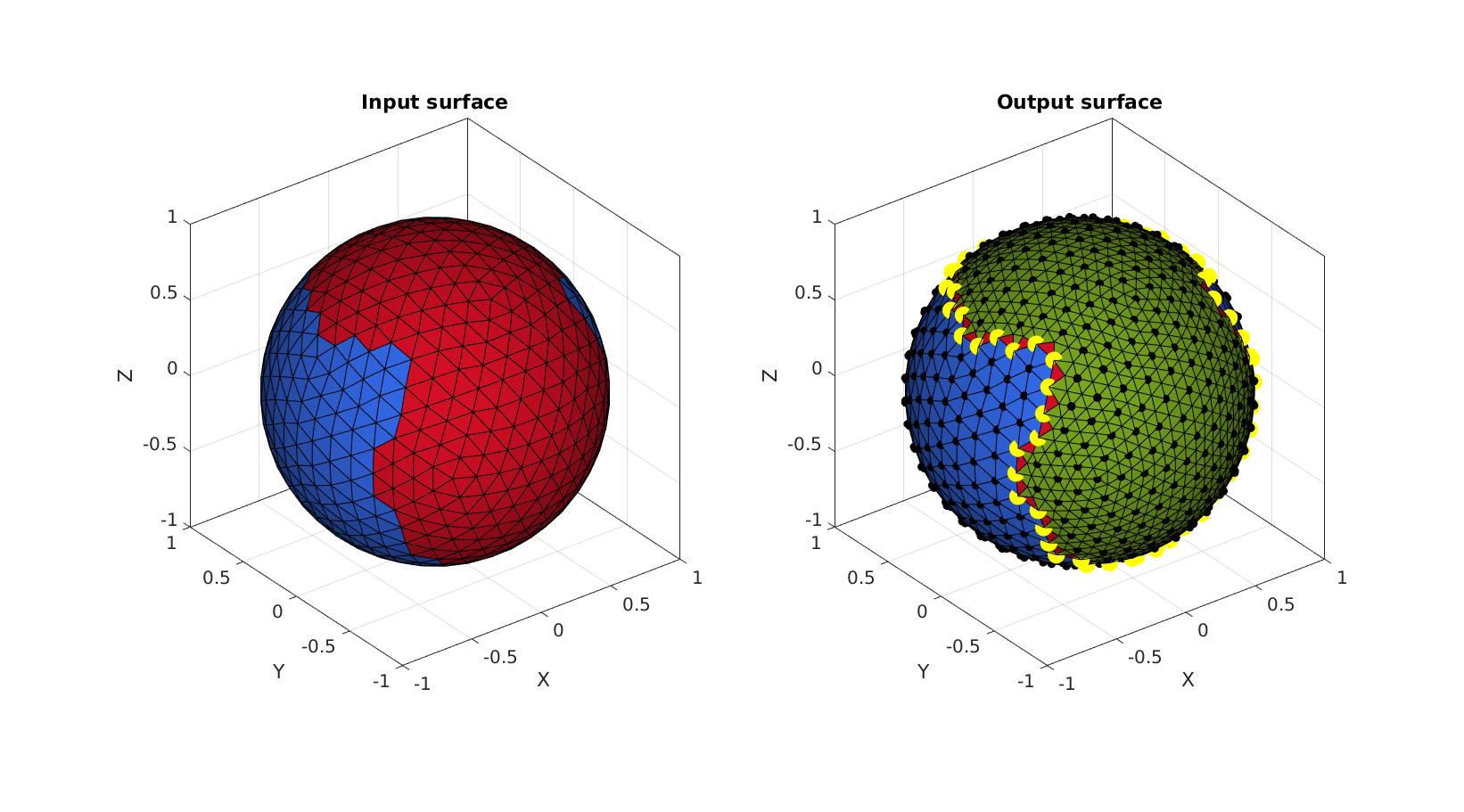
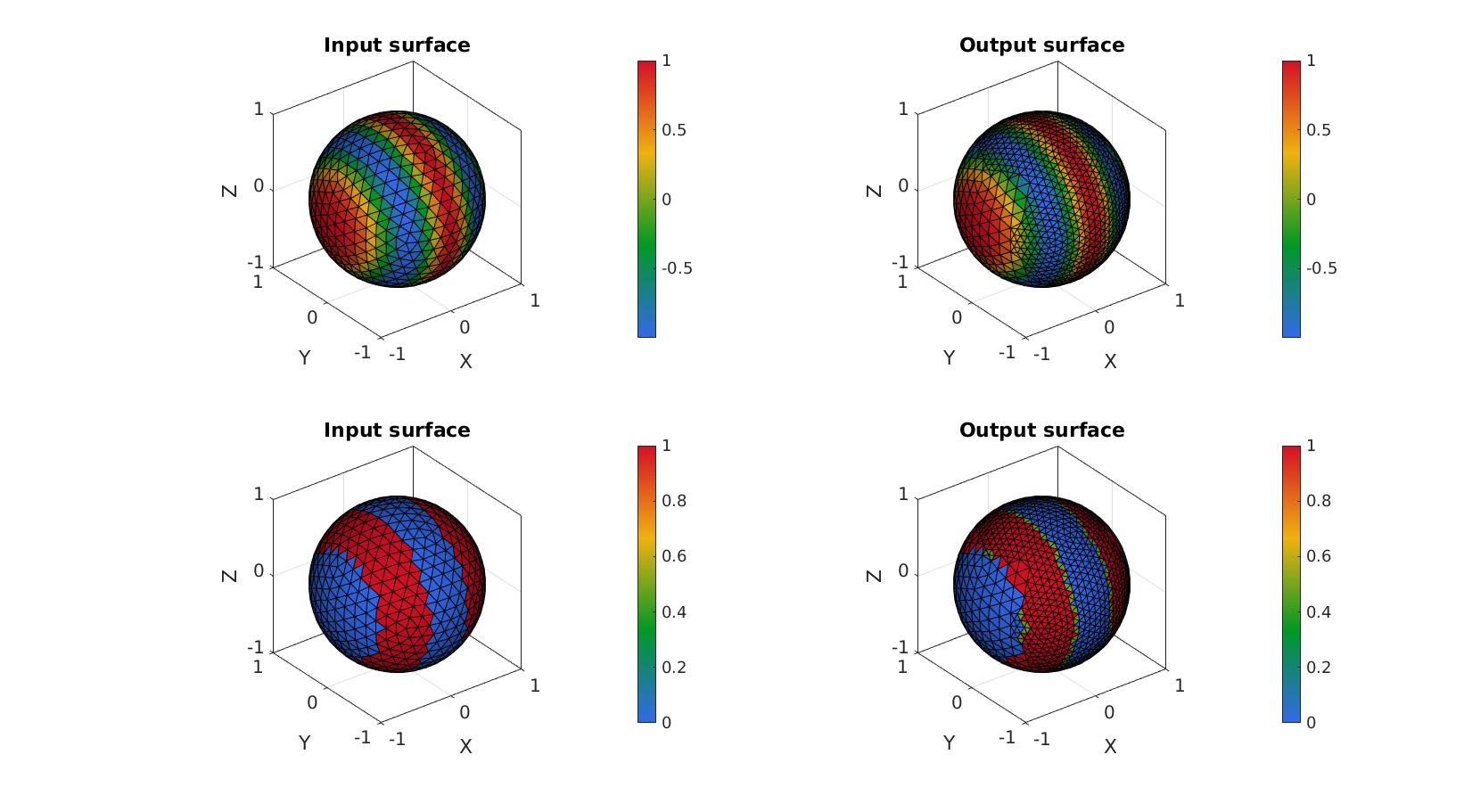
Example: Keeping track of surface data e.g. color
X=V(:,1); XF=mean(X(F),2); %Continuous color C=cos(XF*2*pi);%Continuous color C2=double(C<0); %"Sparse" color to help show averaging at transitions % Refine surface using subTriDual [Ft,Vt,~,~,C_new]=subTriDual(F,V,logicFaces,C); [~,~,~,~,C2_new]=subTriDual(F,V,logicFaces,C2);
Plotting surface models
cFigure; subplot(2,2,1); hold on; title('Input surface','FontSize',fontSize); gpatch(F,V,C); axisGeom(gca,fontSize); colormap gjet; colorbar; camlight headlight; subplot(2,2,2); hold on title('Output surface','FontSize',fontSize); gpatch(Ft,Vt,C_new); axisGeom(gca,fontSize); colormap gjet; colorbar; camlight headlight; subplot(2,2,3); hold on; title('Input surface','FontSize',fontSize); gpatch(F,V,C2); axisGeom(gca,fontSize); colormap gjet; colorbar; camlight headlight; subplot(2,2,4); hold on title('Output surface','FontSize',fontSize); gpatch(Ft,Vt,C2_new); axisGeom(gca,fontSize); colormap gjet; colorbar; camlight headlight; drawnow;
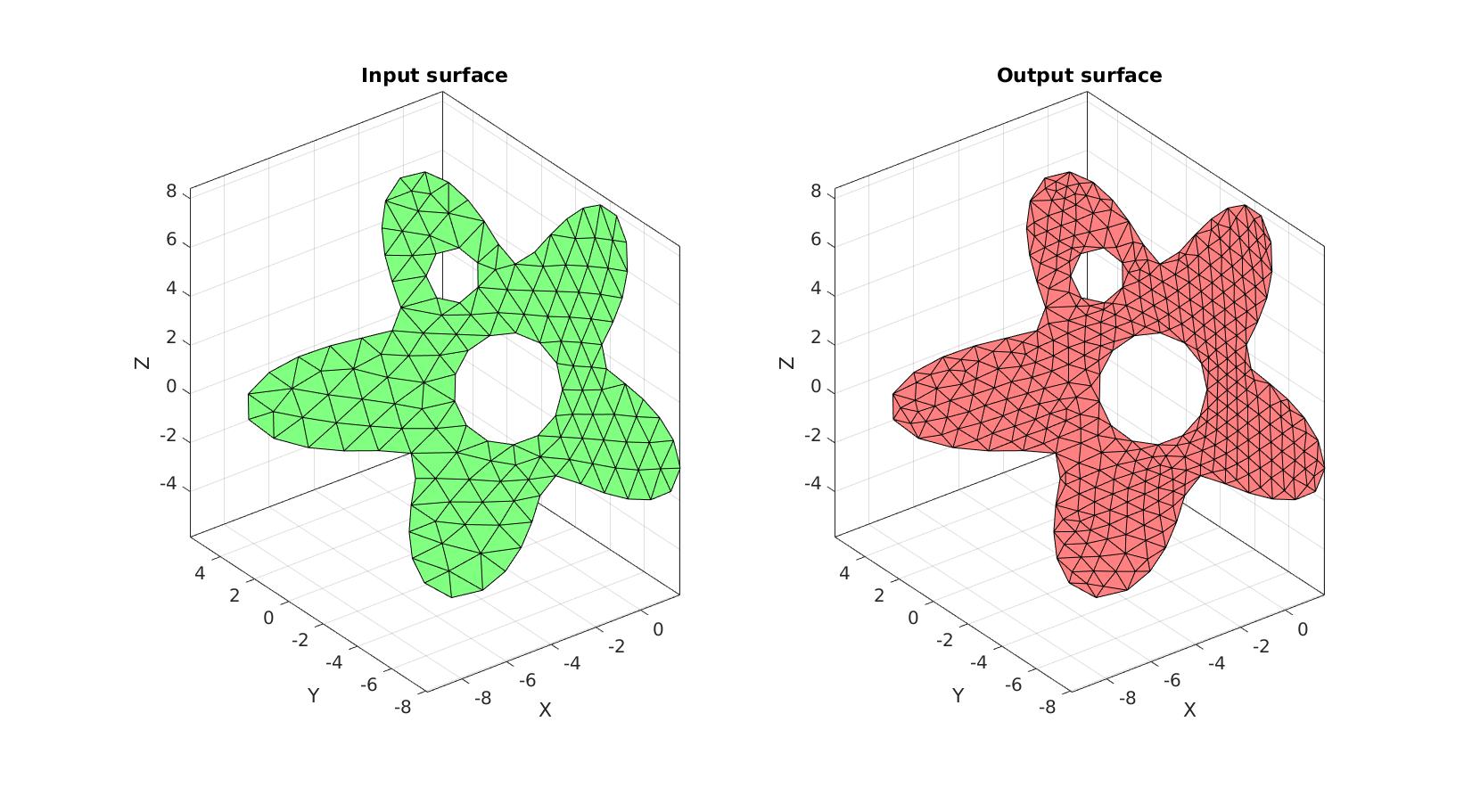
Example: use for non-closed 3D surfaces with voids
Creating complex example surface
%Boundary 1 ns=150; t=linspace(0,2*pi,ns); t=t(1:end-1); r=6+2.*sin(5*t); [x,y] = pol2cart(t,r); z=1/10*x.^2; V1=[x(:) y(:) z(:)]; %Boundary 2 ns=100; t=linspace(0,2*pi,ns); t=t(1:end-1); [x,y] = pol2cart(t,ones(size(t))); z=zeros(size(x)); V2=[x(:) y(:)+4 z(:)]; %Boundary 3 ns=75; t=linspace(0,2*pi,ns); t=t(1:end-1); [x,y] = pol2cart(t,2*ones(size(t))); z=zeros(size(x)); V3=[x(:) y(:)-0.5 z(:)]; %Create Euler angles to set directions E=[0.25*pi -0.25*pi 0]; [R,~]=euler2DCM(E); %The true directions for X, Y and Z axis V1=(R*V1')'; %Rotate polygon V2=(R*V2')'; %Rotate polygon V3=(R*V3')'; %Rotate polygon regionCell={V1,V2,V3}; %A region between V1 and V2 (V2 forms a hole inside V1)
Meshing the region (See also regionTriMesh2D)
%Defining a region and control parameters (See also |regionTriMesh2D|) pointSpacing=1; %Desired point spacing resampleCurveOpt=1; interpMethod='linear'; %or 'natural' [F,V]=regionTriMesh3D(regionCell,pointSpacing,resampleCurveOpt,interpMethod);
logicFaces=true(size(F,1),1); [Ft,Vt,C_type,indIni]=subTriDual(F,V,logicFaces);
Plotting surface models
cFigure; subplot(1,2,1); hold on; title('Input surface','FontSize',fontSize); gpatch(F,V,'gw'); axisGeom(gca,fontSize); subplot(1,2,2); hold on; title('Output surface','FontSize',fontSize); gpatch(Ft,Vt,'rw'); view(2); axisGeom(gca,fontSize); drawnow;
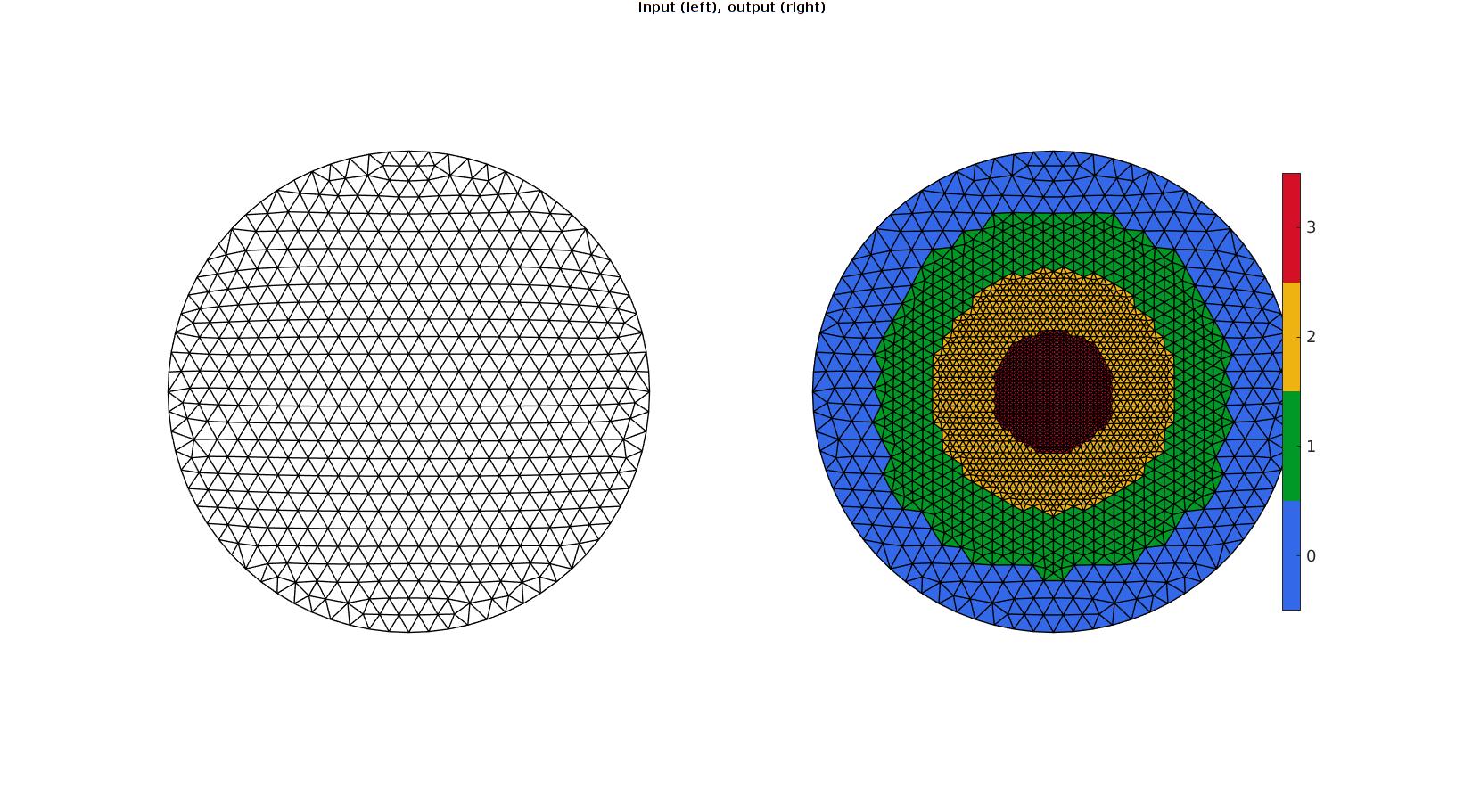
Example: Iterative refinement
Creating example geometry
ns=150;
t=linspace(0,2*pi,ns);
t=t(1:end-1);
r=12;
x=r*sin(t);
y=r*cos(t);
V1=[x(:) y(:)];
regionCell={V1};
pointSpacing=1; %Desired point spacing
resampleCurveOpt=1;
interpMethod='linear'; %or 'natural'
[F,V]=regionTriMesh2D(regionCell,pointSpacing,resampleCurveOpt,interpMethod);
V(:,3)=0;
distanceSplitSteps=[9 6 3]; Ft=F; Vt=V; Ct=zeros(size(Ft,1),1); for q=1:numel(distanceSplitSteps) D=sqrt(sum(Vt.^2,2)); [DF]=vertexToFaceMeasure(Ft,D); logicFaces=DF<(distanceSplitSteps(q)); logicFaces=triSurfLogicSharpFix(Ft,logicFaces); Ct(logicFaces)=Ct(logicFaces)+1; [Ft,Vt,C_type,indIni,Ct]=subTriDual(Ft,Vt,logicFaces,Ct); %Smoothen newly introduced nodes cPar.Method='HC'; cPar.n=50; cPar.RigidConstraints=indIni; [Vt]=tesSmooth(Ft,Vt,[],cPar); %Smoothen boundary nodes on original mesh nodes E=patchBoundary(Ft(C_type==1,:)); indEdge=unique(E(:)); indNodesFaces=Ft(C_type~=1,:); logicValid=ismember(indEdge,indNodesFaces); indEdge=indEdge(logicValid); logicEdge=false(size(Vt,1),1); logicEdge(indEdge)=1; indRigid=find(~logicEdge); cPar.Method='HC'; cPar.n=50; cPar.RigidConstraints=indRigid; [Vt]=tesSmooth(Ft,Vt,[],cPar); end
Plotting surface models
cFigure; gtitle('Input (left), output (right)') subplot(1,2,1); hold on; gpatch(F,V,'w','k',1,1); axisGeom(gca,fontSize); view(2); axis off; zoom(1.1); h=colorbar; h.Visible=0; subplot(1,2,2); hold on; gpatch(Ft,Vt,Ct,'k',1,1); axisGeom(gca,fontSize); view(2); axis off; zoom(1.1); colormap gjet; icolorbar; drawnow;

GIBBON www.gibboncode.org
Kevin Mattheus Moerman, [email protected]
GIBBON footer text
License: https://github.com/gibbonCode/GIBBON/blob/master/LICENSE
GIBBON: The Geometry and Image-based Bioengineering add-On. A toolbox for image segmentation, image-based modeling, meshing, and finite element analysis.
Copyright (C) 2006-2022 Kevin Mattheus Moerman and the GIBBON contributors
This program is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU General Public License for more details.
You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License along with this program. If not, see http://www.gnu.org/licenses/.