Contents
clear; close all; clc;
triSurfCentroid
Below is a demonstration of the features of the triSurfCentroid function
Syntax
[Vc]=triSurfCentroid(F,V);
Description
The triSurfCentroid function enables refinement of triangulated data
Examples
clear; close all; clc;
Plot Settings
fontSize=15; faceAlpha=0.2; markerSize=35;
Example: Calculating the centriod of a triangulated surface
Building example geometry, in this case a sphere
%Defining geodesic dome r=1; %sphere radius n=2; %Refinements [F,V,~]=geoSphere(n,r);
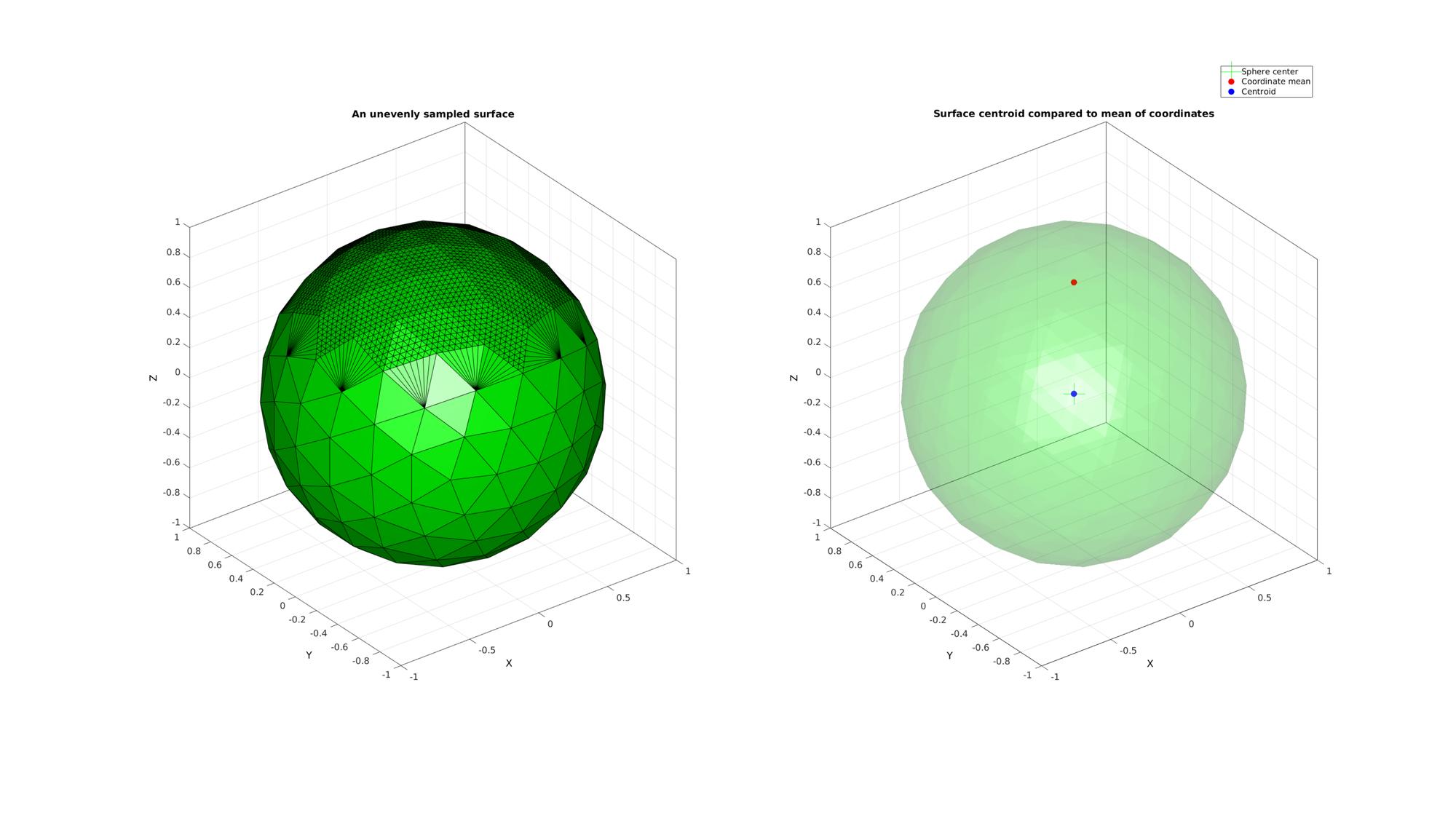
The geoSphere function creates a homogeneously sampled sphere, hence the mean of the coordinates coincides with the centroid. To see the difference with the centroid we'd need to change the sampling.
% Using |subTriLocal| to refine a top region of the sphere which will % offset the mean of the coordinates from the centroid. nRefine=3; %Number of local refinement steps for q=1:1:nRefine %Create logic for faces to refine L=V(:,3)>0.5; LF=all(L(F),2); indFaces=find(LF); %Refining the surface locally inputStruct.F=F; inputStruct.V=V; inputStruct.indFaces=indFaces; [outputStruct]=subTriLocal(inputStruct); F=outputStruct.F; V=outputStruct.V; end
Now the mean of the coordinates and the centroid will be calculated.
Vm=mean(V,1); %Mean of the coordinates [Vc]=triSurfCentroid(F,V); %Centroid of the surface
Plotting results
cFigure; subplot(1,2,1); hold on; title('An unevenly sampled surface','fontSize',fontSize); gpatch(F,V,'g','k',1); axisGeom(gca,fontSize); camlight headlight; subplot(1,2,2); hold on; title('Surface centroid compared to mean of coordinates','fontSize',fontSize); gpatch(F,V,'g','none',faceAlpha); h1=plotV([0 0 0],'g+','MarkerSize',markerSize); h2=plotV(Vm,'r.','MarkerSize',markerSize); h3=plotV(Vc,'b.','MarkerSize',markerSize); legend([h1 h2 h3],'Sphere center','Coordinate mean','Centroid'); axisGeom(gca,fontSize); camlight headlight; drawnow;

GIBBON www.gibboncode.org
Kevin Mattheus Moerman, [email protected]
GIBBON footer text
License: https://github.com/gibbonCode/GIBBON/blob/master/LICENSE
GIBBON: The Geometry and Image-based Bioengineering add-On. A toolbox for image segmentation, image-based modeling, meshing, and finite element analysis.
Copyright (C) 2019 Kevin Mattheus Moerman
This program is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU General Public License for more details.
You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License along with this program. If not, see http://www.gnu.org/licenses/.